librairie is a bookshop and not library.
and, yes, it’s confusing.


librairie is a bookshop and not library.
and, yes, it’s confusing.


writing about politics on lemmy is liking pissing in the wind. This is my last comment under this map which speaks for itself.
if it was “bullshit” or if it wouldn’t change anything, these nations would have recognized Palestine years ago. The fact that they waited so long shows that it was “something”.
Again, if it wouldn’t change anything, Israel wouldn’t react to it.
I can’t understand this need to minimize. If Israel exists today, it’s because of these nations that are turning a page today. Circumstances have changed but they still are the shadows of nations that carelessly designed what they call “middle east”. This map and it’s latest modifications should be taken into consideration with numerous other maps that’s drawn since 19th century.
defeatism is more tiring than defeat itself.


Yet this is the great diplomatic Master stroke of our left of center governments in the West.
Macron is left of center⁉️ He was central for this “stroke” and if you think that he is “left of center”, your map is upside down.
Anything short of sending their Navy and Military to land food on the beach and physically defend handing it out is bullshit at this point.
if you think of Palestine’s recognition by these nations as “bullshit” at this point… i wonder who i’m writing to. It of course is not enough; but it’s not “bullshit” either, especially if you consider who is the emperor since January.

misunderstanding is my fault. i implied but haven’t finished my sentence. Should be better now after the edit 👆


can you explain what you think i’ve missed?


sad to read all that but thanks for the information. I try to avoid political communities because of all the bigotry and hate they attract but if staying on a lemmy instance would mean supporting lemmy devs (even if i disagree with them)… edit to finish the sentence: it would be difficult to justify staying on lemmy
i feel good about sh.itjust.works , but it’s still lemmy 🤷
can that be ☞ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Laetiporus_sulphureus ?
rosemary indeed + white wine, onion, pepper and nuts.
we’ll try with butter next time
i’ve already picked in the past from a neighbor tree. Red fluid that oozes just after cutting it from the tree and the taste of it raw + the inaturalist identification. So, i feel pretty confident about it. But i would like to know more, if you are suspicious about it. Maybe i should stop eating these?
what do you think it is?
that’s what the oak said


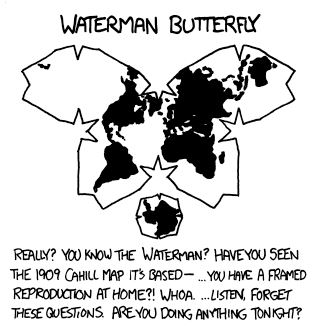
I get Spain, but why is it that so often with these maps Eastern Europe shares the same word as the Arab world?
Ottoman empire ruled the eastern Europe for some centuries and Ottoman language was a mixture of Turkish, Persian and Arabic.

but i assume that the elephant is Indian influence rather than Arabic. IIRC, that’s also where the game is conceived
edit, yes, it literally is an elephant ☞ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chaturanga


“intervention”


just a guess
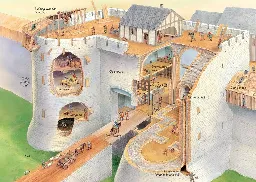
No footpaths or streets were used between the dwellings, which were clustered in a honeycomb-like maze. Most were accessed by holes in the ceiling and doors on the side of the houses, with doors reached by ladders and stairs. The rooftops were effectively streets.


Nantes is wheat fields 🤔 all of Normandy and Brittany too
my bad, for paris i had to zoom a little bit more


where is California in all this?
why exclude Paris too?
seems too arbitrary… what are the criteria?


Malta is in cahoots with France on “a crusade against the Jewish state.”
😮
downloading
a link for antennaPod users ☞ The New Yorker: Fiction: https://publicfeeds.net/f/6232/new-yorker-fiction
Episode webpage: https://the-new-yorker-fiction-4473086b.simplecast.com/episodes/sterling-holywhitemountain-reads-roberto-bolano-dUHPxCNW
thanks for sharing this
I’ve got one question to any other reader/looker about this : Let’s say, for the sake of convenience, that she’s called Carla Devade. She could well be the youngest member of the group. Her hair is short,
I see Carla’s hair as long and wrapped in a bun
a weirdo indeed ☞